Heat Pump vs Mini Split: Unbiased HVAC Showdown for 2024

Heat Pump vs Mini Split: When it comes to heating and cooling your home or office, choosing the right HVAC system is essential for both comfort and energy efficiency. Two popular options in the market are heat pumps and mini split systems. Both systems have their unique features and benefits, offering various solutions for different types of buildings and temperature needs. Comparing these two systems will help you make a really informed decision on which one is best suited for your needs.
Heat pumps are a great versatile way that can provide both heating and cooling to a space for your needs. They're made to transfer heat from one area to another, making them a lot more energy-efficient option than traditional furnaces and air conditioners. Mini split systems, on the other hand, are ductless HVAC systems that can provide targeted heating and cooling to specific areas, making them ideal for spaces with unique temperature requirements or for those looking to streamline their HVAC setup.

Key Takeaways from Heat Pump vs Mini Split
- Heat pumps and mini split systems offer versatile heating and cooling options for various building types and temperature needs.
- When comparing installation processes, costs, and efficiency can help you determine the best HVAC system for your space.
- Both systems provide customizable temperature control, but mini splits offer additional zoning capabilities for targeted comfort.
Understanding HVAC Systems
When it comes to HVAC systems, there are two popular options: heat pumps and mini-splits. HVAC systems will help you maintain a comfortable indoor environment in your home while also keeping energy costs down. Let's look into some key differences and features between these types of systems.
Heat pumps are versatile systems that can both heat and cool your home. They do this by transferring heat energy from one location to another. During the winter, a heat pump absorbs heat from the outdoor air and delivers it inside your home. In summer, it reverses the process and takes heat from indoors, releasing it outside. Heat pumps can be either central systems or mini-splits, which we will discuss further.
Mini-splits, on the other hand, are typically ductless systems. They consist of an indoor unit and an outdoor unit, connected by refrigerant lines. Many mini-splits can function as heat pumps, offering both heating and cooling capabilities. However, not all mini-splits are heat pumps; some only provide cooling.
Let's compare some key features of heat pumps and mini-splits:
- Efficiency: Heat pumps and mini-splits are known for their energy efficiency. Mini-splits can be up to 30% more efficient in cooling compared to traditional air conditioners. Heat pumps, on the other hand, can save you up to 60% on heating costs when compared to electric resistance-based systems.
- Control: With mini-splits, each indoor unit can have its own temperature settings, giving you individualized control over different areas in your home. Heat pumps, in contrast, usually integrate with a central thermostat.
- Installation cost: The average installation cost for heat pumps ranges from 1,500 to 10,000, while mini-splits average between 2,000 and 8,000.
So In conclusion, whether you choose a heat pump or a mini-split will depend on your specific needs and preferences. When you are considering factors such as energy efficiency, control, and installation costs to determine the best HVAC system for your home.
HVAC Banner
The Basics of Heat Pumps
Heat Pump vs Mini Split: As someone looking into heating and cooling options, you've likely heard about heat pumps. But what exactly is a heat pump, and how does it work? Let's dive into the basics.
A heat pump is a versatile HVAC system that can efficiently regulate your home's temperature by transferring heat energy. Unlike traditional systems that generate heat, these devices work by moving heat from one place to another. In the winter, they extract warmth from the outdoor air or ground and transfer it inside your home. Conversely, in the summer, they remove heat from your interior space and release it outdoors, keeping your home cool and comfortable.
Heat pumps are known for their energy efficiency, as they use less energy than other heating and cooling systems. This is because they just move heat, rather than having to generate it. When properly installed and maintained, heat pumps can provide consistent temperatures, maximizing comfort.
Here's a quick rundown of the main components of a heat pump system:

- Outdoor unit: Contains the compressor, which circulates the refrigerant, and the coil, which helps transfer heat.
- Indoor unit: Houses the air handler, which circulates the conditioned air, and another coil, where heat transfer occurs.
- Refrigerant: The substance responsible for absorbing and releasing heat as it travels between the outdoor and indoor units.
- Ductwork (optional): Depending on the type of heat pump, you might have ducts or ductless system options.
Heat pumps operate most efficiently in moderate climates, offering a cost-effective and eco-friendly alternative to traditional heating and cooling systems. However, their efficiency may decline in extreme weather conditions. In such cases, you could combine your heat pump with a supplementary heating system, like a furnace or electric heater, to ensure optimal performance.
So in conclusion, if you're looking for an energy-efficient solution that can maintain your home's temperature, heat pumps are a solid choice. Evaluate your specific needs, climate, and budget to decide whether this system is suitable for you.
Consult With An Expert
Heat Pump Installation Process

When you're planning to install a heat pump system, it's important to understand the process. Firstly, determine whether you need a ducted or mini-split system. Ducted systems require ductwork throughout your home, while mini-split systems use individual indoor air handlers, making them a popular choice for easier installation.
Keep in mind that a ducted system may be more appropriate for your home if you want to heat and cool multiple rooms simultaneously. A key aspect of installation for these systems is the design and installation of ductwork. Make sure to work with an experienced professional to ensure proper duct design, as improper ductwork can lead to inefficiency and decreased comfort.
The process of installing a heat pump typically involves the following steps:
- System design: Work with an HVAC professional to determine the appropriate size and design of the heat pump system for your home.
- Ductwork (if applicable): Have your HVAC contractor assess your existing ductwork or design and install new ductwork according to your heat pump system's requirements.
- Outdoor Unit: The outdoor unit, or compressor, will be placed on a level surface outside your home, with proper clearance and connection to your home's electrical system.
- Indoor Units: For a mini-split system, your contractor will install individual air handlers in the desired rooms, ensuring proper mounting and clearance for efficient operation.
- Connecting: Tubes or cables will be run between the outdoor and indoor units to complete the system's installation.
- System check: Ensure the system is running effectively and efficiently by testing it according to the manufacturer's guidelines.
Remember that proper installation by an experienced professional is crucial for your heat pump system's performance and longevity. Errors in installation can lead to increased energy costs and decreased comfort in your home. So, choose a reputable contractor with experience in heat pump and mini-split installations.
Cost Considerations
When you're comparing heat pumps and mini-splits, it's crucial to take into account the various costs associated with each system. Let's explore the different financial aspects you should consider, from installation to maintenance, to make an informed decision.
Initial installation costs: Heat pumps typically have a higher initial cost than mini-splits. On average, heat pump installation ranges between ,500 and ,000, while mini-split installation averages between ,000 and ,000. Keep in mind, the type and size of the units, complexity of the installation, and your location all play a role in determining the final price.
Energy efficiency: Both heat pumps and mini-splits offer significant energy savings compared to traditional heating and cooling systems. For example, you can cut your heating costs up to 60% with a mini-split compared to electric resistance-based systems. On average, cooling costs can also be 30% less when compared to traditional air conditioners. However, heat pumps tend to be slightly more efficient than mini-splits.
Operation costs: Along with their superior energy efficiency, both heat pumps and mini-splits can help you save on your monthly utility bills. Please be aware that factors such as insulation, climate, and temperature settings can affect the operating cost, so it's essential to evaluate the potential savings based on your specific circumstances.
Maintenance costs: Regular maintenance is necessary for both systems to maintain efficiency, ensure safety, and extend their lifespan. However, mini-splits often have lower maintenance costs compared to heat pumps since they don't require ductwork. Remember that when you neglect maintenance can lead to higher energy consumption, reducing the potential for cost savings in the long run.
Ultimately, it's really is up to you to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each system. Especially concerning your budget constraints and long-term cost savings. Don't forget to take into account any potential rebates or incentives that may be available in your area to help offset the initial cost.
Speak With An Expert
Maximizing Efficiency with Heat Pumps

Heat Pump vs Mini Split: When it comes to heating and cooling your home, energy efficiency is a critical factor to consider. Heat pumps can be an excellent choice for maximizing efficiency, especially in moderate climates. In this section, we'll continue to discuss some of the key aspects to making your heat pump system more energy-efficient and cost-effective.
First, it's essential to select a heat pump with a high SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) and EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio) rating. The ratings on these can give you an idea of how efficiently the unit will use. Electricity for cooling and heating is a huge deciding factor in this. The higher the SEER and EER, the more energy-efficient the unit will be in operation.
Here are some points to consider for maximizing efficiency:
- Inspection and maintenance: Regular inspection and maintenance of your heat pump system can help identify and address any issues that may affect efficiency. This includes checking the filters, fan motor, and coils for any dirt or debris that could hinder performance.
- Temperature settings: Adjusting your thermostat settings can have a significant impact on your system's energy use. A good rule of thumb is to set your thermostat to the lowest comfortable temperature during the heating season and the highest comfortable temperature during the cooling season.
- Proper insulation: Ensuring sufficient insulation in your home can minimize energy losses. Inspect your attic, walls, and floors for any gaps or weak spots where heat may escape, which would cause your heat pump to work harder than necessary.
To further boost efficiency, you could also consider:
- Installing a programmable thermostat to automatically adjust temperature settings throughout the day, which can help reduce electricity consumption.
- Using window treatments such as blinds, shades, and curtains to help regulate indoor temperatures and decrease the load on your heat pump.
- Sealing air leaks around doors and windows with weatherstripping and caulk.
Keep in mind, a well-maintained and properly adjusted heat pump system does wonders for your home's energy efficiency. Taking these steps, you will see major savings on your electricity bills while doing your part to reduce carbon emissions and promote a greener future for all. Heat pumps are an outstanding solution for homeowners seeking an energy-efficient and environmentally friendly choice for their HVAC needs.
Exploring Different Types of Heat Pumps
Heat Pump vs Mini Split: As you dive into the world of heat pumps, you'll come across various types, each with its own unique features and benefits. This brief guide will help you understand the differences between the main types of heat pumps: geothermal heat pumps, air source heat pumps, ducted heat pumps, ductless heat pumps, and cold-climate heat pumps.
Geothermal Heat Pumps: A geothermal heat pump harnesses the earth's natural heat to provide heating and cooling for your home. By using the temperature stability of the ground, it efficiently and eco-friendly delivers conditioned air. While the installation cost can be higher than for other options, the long-term energy savings make it an attractive choice.

Air Source Heat Pump: Moving on to air source heat pumps, these systems extract heat from the outdoor air and transfer it inside for heating purposes, or vice versa for cooling. They work best in moderate climates, as their efficiency drops when the temperature goes below freezing.
-Ducted Heat Pumps: Ideal for larger homes or those with existing ductwork, ducted heat pumps distribute conditioned air through a network of ducts. This system can provide efficient heating and cooling throughout the entire house, making for a comfortable living environment.
-Ductless Heat Pump: Also known as mini splits, ductless heat pumps are perfect for homes that lack ductwork or need temperature control in specific areas. With their zoning capabilities, you can customize the temperature in each space or room, leading to increased efficiency and comfort.
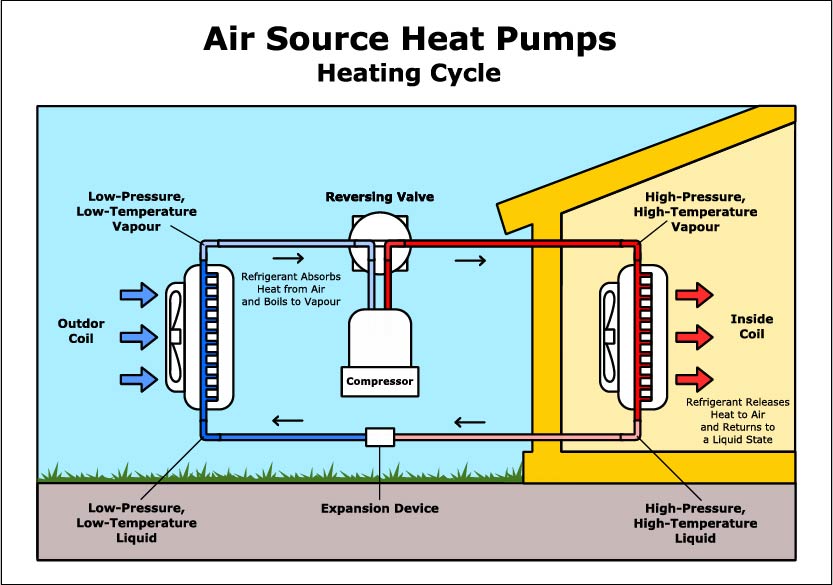
Cold-Climate Heat Pumps: Finally, cold-climate heat pumps are designed for those living in areas with harsh winters. They can operate efficiently even when the temperature drops below freezing, providing reliable heating without the need for additional heating systems.
To choose the right type of heat pump for your needs, consider factors like the climate, your home's layout, and existing infrastructure. By understanding the different types of heat pumps, you're well on your way to make an informed decision that best suits your comfort needs and budget.

Heat Pump Components
Heat Pump vs Mini Split: Let me tell you about heat pump components, as if Joe Rogan was an HVAC contractor. The main components of a heat pump system are the outdoor unit, the indoor unit, and the refrigerant that flows between both units.
The outdoor unit is the workhorse of the system. It houses the compressor and the condenser. The compressor does the heavy lifting by increasing the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant gas. This creates a high-pressure, high-temperature gas that then flows to the condenser. In the condenser, this hot gas releases its heat to the outside air and gets converted into a cooler liquid.
Now, let's move to the indoor unit. It contains an air handler, which is responsible for distributing the heated or cooled air throughout your living space. Apart from that, the indoor unit also has an evaporator coil. The refrigerant in its liquid state absorbs heat from your home's air as it flows through the evaporator coil, effectively cooling down the air. And then, the process repeats itself.
To sum it up, here's an overview of the key components involved in a heat pump:
-
Outdoor Unit
- Compressor - increases pressure and temperature of the refrigerant gas
- Condenser - releases heat from high-pressure refrigerant gas, converting it into a liquid
-
Indoor Unit
- Air Handler - distributes heated or cooled air throughout your living space
- Evaporator Coil - absorbs heat from the indoor air, cooling it down
Furthermore, the refrigerant acts as the lifeblood of a heat pump system. It flows between the outdoor and indoor units in a continuous cycle, absorbing and releasing heat to provide the desired temperature inside your home.
Now you have a better understanding of the heat pump components and how they work together to heat or cool your space. Remember, knowing the ins and outs of your system can help you make informed decisions about maintenance, repairs, and overall efficiency. So, keep this information in mind and stay on top of your heat pump's performance.
Customizing with Mini-Split Systems
Heat Pump vs Mini Split: When considering heating and cooling options for your home, you might be looking for a system that offers more flexibility and control than traditional central air systems. Ductless mini-split systems can be the solution you need, as they provide targeted heating and cooling for individual rooms or zones in your home.
One of the advantages of mini-split systems is their ability to create multiple temperature zones within your home. Each indoor unit, often referred to as a "head," connects to a single outdoor unit and can be controlled individually. This means you can easily customize the temperature in different rooms, making your home more comfortable and energy-efficient. For those with larger homes or multiple rooms, you may want to consider a multi-zone mini split system, which uses multiple heads connected to a single outdoor unit.
Since mini-split systems are ductless, you can save on energy losses that can occur in traditional ducted systems. Additionally, installation is typically easier and more affordable than installing ductwork, making them a popular choice for homes without existing ducts or for renovations and additions.
Here's a summary of the benefits of mini-split systems:
- Energy-efficient: Mini-splits can be more efficient than traditional HVAC systems.
- Zone control: Precise temperature control for individual rooms or zones.
- No ducts: Eliminates energy losses from leaky ducts and makes installation easier.
- Versatile: Suitable for new construction, renovations, or homes without existing ductwork.
While ductless heating and cooling systems offer numerous benefits, it's essential to consider your specific needs and budget. If you're looking for zone control and ease of installation, mini-splits might be the perfect solution for your home.
Speak with Industry Leading Experts
Temperature Control and Zoning Capabilities

Heat Pump vs Mini Split: When you look into heating and cooling systems, temperature control and zoning capabilities are important factors to consider. With a heat pump and a mini-split, you have different options for managing the climate in your home.
Heat pumps typically integrate with a central thermostat, allowing for uniform temperature control throughout your entire home. This provides a consistent level of comfort, but may not be as energy efficient as controlling individual zones separately. On the other hand, mini-split systems offer you greater zoning capabilities and the flexibility to control the temperature in each room or area of your house independently, leading to increased energy efficiency and customized comfort.
Here's a table summarizing the differences between these systems in terms of temperature control and zoning:
| System | Temperature Control | Zoning Capabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Pump | Central thermostat | Limited |
| Mini Split | Individual controls | high |
In terms of climate control, mini splits can be broken down into two categories:
-
Single zone mini split: This type of system has one indoor unit and one outdoor unit, making it suitable for domestic and commercial applications in a single area or room (source).
-
Multi-zone mini split: This setup includes multiple indoor units connected to a single outdoor unit, allowing for optimal climate control in various individual rooms or zones.
The advantage of using mini splits for zone control capabilities is that you can adjust the temperature in each area according to your preference and the specific needs of those using the space. This means no more arguments about the thermostat settings! So, if you’re looking for a heating and cooling solution that allows you to customize temperature levels in different parts of your home, a mini-split system might be your best bet.
Maintenance and Reliability
When it comes to maintenance and reliability of heat pumps and mini-splits, certain factors can help you decide which type is the best option for you. In this section, we'll explore key aspects such as regular maintenance, durability, and maintenance costs that you should consider before making a decision.
Regular Maintenance Heat pumps and mini-splits both require regular maintenance to ensure optimum performance and longevity. For a heat pump, you'll need to inspect and clean the coils, filters, and blower components periodically. Mini-splits, on the other hand, require the maintenance of filters, indoor coil, and outdoor coil. Since mini-splits also lack ducts, there's less need for duct cleaning, which is a common requirement for traditional heat pumps.
Reliability and Durability Heat pumps are known for their efficiency and performance in moderate climates, ensuring consistent temperature control throughout your home. Mini-splits, while suitable for small spaces or specific rooms, can still face some challenges in extreme weather conditions.
Durability-wise, both heat pumps and mini-splits have a lifespan of approximately 10-15 years, depending on brand quality and upkeep. It is very crucial to select a reliable manufacturer if you expect your investment to stand the test of time.
Maintenance Costs and Needs Heat pumps generally have higher maintenance costs due to their more extensive systems, including ductwork maintenance. On the other hand, mini-splits boast lower maintenance costs since their inherent ductless design simplifies upkeep and reduces potential repair expenses.
Here's a quick comparison:
| Features | Heat Pump | Mini-Split |
|---|---|---|
| Regular Maintenance | Coils, filters, blower components, and duct cleaning | Filters, indoor and outdoor coils |
| Reliability | Excellent in moderate climates | Good for small spaces/zones |
| Durability | 10-15 years, depending on brand | 10-15 years, depending on brand |
| Maintenance Costs | Higher due to ductwork and more components | Lower, as they're ductless |
Therefor In conclusion, before making a huge decision on which HVAC system to install, consider your home's size, climate conditions, and the importance of both maintenance needs and costs in your budget. Keep this information in mind to help you choose between a heat pump and a mini-split for your ideal heating and cooling solution.
Speak With An Expert Now
Incentives, Rebates, and Tax Credits
When it comes to deciding between a heat pump and a mini-split, you should also consider the various incentives, rebates, and tax credits available that can help offset the cost of your investment. It is always essential to be well-informed about these financial benefits, as they can significantly impact which option is more affordable for you in the short & long run.
First off, check the ENERGY STAR website for information regarding federal tax credits on energy-efficient heating equipment, including air source heat pumps. According to their information, you could be eligible for:
- A tax credit of up to ,200 for insulation improvements.
- Up to ,000 per year for qualified heat pumps.
Keep in mind that tax credits can sometimes be combined with other home improvement projects such as window or door replacements, allowing you to save even more money over the long run.
Additionally, certain states offer their own incentives and rebates for energy-efficient heating systems for residential use. Consumer Reports, in their article, explains that spending ,000 on a heat pump and a heat pump water heater could return ,750, depending on your state's rebate program.
Lastly, the IRS also has energy-efficient home improvement credits available. You can claim up to ,200 for certain energy-efficient home improvements and up to ,000 yearly for qualified heat pumps, biomass stoves, or biomass boilers.
With all these incentives, rebates, and tax credits available, making the decision between a heat pump and a mini-split should be much easier and more cost-effective. So take advantage of these benefits, find the most energy-efficient option for your home, and stay warm during those chilly months.
Frequently Asked Questions

What's the real difference in cost between a heat pump and a mini-split system, man?
When comparing the average cost range for installation, heat pumps typically cost between ,500 and ,000, while mini-splits are slightly cheaper with installation costs ranging from ,000 to ,500. Keep in mind that the actual cost varies depending on the specific make and model you choose, as well as the size of your home and the complexity of the installation.
Can you break down the pros and cons of heat pumps compared to mini-splits like I'm in the octagon with them?
You got it! Heat pumps are known for their efficiency, especially in moderate climates. They distribute conditioned air evenly throughout your home, ensuring consistent temperature control. Mini-splits have their advantages too, offering more flexibility with zoning capabilities, and they're typically easier to install in existing structures.
However, heat pumps can also be more expensive upfront, and their efficiency might decrease in extremely cold temperatures. On the flip side, mini-splits might not be as efficient in heating large spaces, and they require multiple indoor units for a larger home.
When it comes to getting the most bang for your buck in efficiency, you rolling with a heat pump or a mini-split?
It really depends on your individual needs and the climate you live in. Heat pumps are generally more efficient, especially in moderate climates. Mini-splits can be a great alternative if you need zoned cooling and heating or if you're working with a limited space, but overall, heat pumps might edge them out in terms of energy efficiency.
Is there a clear champ in the ring when we're talking about a ducted or ductless system for heat pumps?
Ducted and ductless systems each have their pros and cons. A ducted heat pump can provide even temperature control throughout your home and blend seamlessly with your existing ductwork. Meanwhile, ductless systems don't require any ducts, making them easier to install and a more attractive option for homes without existing ductwork.
That said, there isn't a one-size-fits-all answer here. Consider factors like your home's layout and existing infrastructure to figure out which option best suits your needs.
Why aren't more folks stepping into the ring with mini-splits if they're so efficient?
Even though mini-splits are quite efficient and offer zoned temperature control, their higher upfront costs can be a deterrent for some homeowners. Additionally, they might not be ideal for larger homes or those in need of a complete heating and cooling system, as multiple indoor units would be required.
In the battle of monthly bills, which heavyweight wins – the mini-split or the central AC?
While central AC systems can be more powerful, mini-splits generally offer greater energy efficiency and lower operating costs. On average, mini-split cooling costs can be 30% less than traditional air conditioners. Keep in mind, energy consumption varies depending on factors like the size of your home, insulation, and weather conditions. It is extremely important to weigh those options alongside your personal preferences to make an informed decision before you buy.



Leave a comment